Por favor, use este identificador para citar o enlazar este ítem:http://uvadoc.uva.es/handle/10324/31351
Título
Altered predictive capability of the brain network EEG model in schizophrenia during cognition
Autor
Año del Documento
2018
Editorial
Elsevier
Descripción
Producción Científica
Documento Fuente
Schizophrenia Research, In Press
Abstract
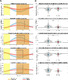
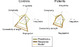
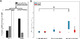
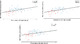
The study of the mechanisms involved in cognition is of paramount importance for the understanding of the neurobiological substrates in psychiatric disorders. Hence, this research is aimed at exploring the brain network dynamics during a cognitive task. Specifically, we analyze the predictive capability of the pre-stimulus theta activity to ascertain the functional brain dynamics during cognition in both healthy and schizophrenia subjects. Firstly, EEG recordings were acquired during a three-tone oddball task from fifty-one healthy subjects and thirty-five schizophrenia patients. Secondly, phase-based coupling measures were used to generate the time-varying functional network for each subject. Finally, pre-stimulus network connections were iteratively modified according to different models of network reorganization. This adjustment was applied by minimizing the prediction error through recurrent iterations, following the predictive coding approach. Both controls and schizophrenia patients follow a reinforcement of the secondary neural pathways (i.e., pathways between cortical brain regions weakly connected during pre-stimulus) for most of the subjects, though the ratio of controls that exhibited this behavior was statistically significant higher than for patients. These findings suggest that schizophrenia is associated with an impaired ability to modify brain network configuration during cognition. Furthermore, we provide direct evidence that the changes in phase-based brain network parameters from pre-stimulus to cognitive response in the theta band are closely related to the performance in important cognitive domains. Our findings not only contribute to the understanding of healthy brain dynamics, but also shed light on the altered predictive neuronal substrates in schizophrenia.
Revisión por pares
SI
Patrocinador
This research project was supported in part by “Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad” and FEDER under project TEC2014-53196-R, by ‘European Commission’ (POCTEP 0378_AD_EEGWA_2_P), by ‘Consejería de Educación de la Junta de Castilla y León’ (VA037U16), by “Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias (Instituto de Salud Carlos III)” under projects FIS PI11/02203 and PI15/00299, and by “Gerencia Regional de Salud de Castilla y León” under projects GRS 932/A/14 and GRS 1134/A/15. A. Lubeiro was in receipt of a grant from the Consejería de Educación (Junta de Castilla y León). J. Gomez-Pilar was in receipt of a grant from University of Valladolid.
Version del Editor
Propietario de los Derechos
Schizophrenia Research
Idioma
eng
Derechos
restrictedAccess
Collections
Files in this item